CUT&Tag-IT® R-loop Service Overview
Active Motif’s CUT&Tag-IT® R-loop Service can help you map R-loops genome-wide, using a unique, specific antibody that detects a DNA-RNA hybrid. Similar to our CUT&Tag-IT® Service for mapping histone modifications, tagmentation is performed by our adapter-loaded Tn5 Transposase enzyme, which is directed to R-loop/antibody complexes by a secondary antibody. The loci participating in the R-loop structure is then cut and tagged by the Tn5 and this library, created in situ, is then sequenced.
What are R-loops?
R-loops are 3-stranded structures containing displaced ssDNA and a DNA-RNA hybrid. These structures form normally during transcription initiation, IgG class switching, and mitochondrial DNA replication. They also appear normally at telomeres. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to DNA displacement loops or D-loops; where the "R" in this case represents the RNA in the third strand of the loop. Abnormal R-Loop formation is associated with DNA damage, replication fork stalling, impaired DNA repair, and genomic instability. Cancer cells with aberrantly activated transcriptional programs can have transcription-replication conflicts, enhancing the likelihood of abnormal R-loop formation.
Examples of how R-loop analysis can support epigenetics & biomarker research:
R-loops as Biomarkers
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 help to resolve R-loops that form at transcription start/termination sites
- ATR, a DNA damage response kinase, may correlate with R-loop formation
- Cells sensitive to ATR inhibition may demonstrate an increase in R-loop levels
- Cancer cells with known, high R-loop levels display sensitivity to ATRi
- PARP inhibition, which is a synthetic lethal in BRCA-deficient cells, is also lethal to cells with high R-loops, even those with functional BRCA proteins
- Cancers with high R-loop levels are being investigated for PARPi or ATRi sensitivity
R-loops and Epigenetics
- R-loops prevent DNA methylation at active promoters, and DMNT1 has lower affinity for RNA-bound DNA
- R-loops also recruit GADD45A (an R-loop “reader”) which enhances TET1 (Ten Eleven Translocation 1) conversion of 5-mC to 5-hmC
- R-loops recruit the PRC2/EZH2 complex to methylate H3K27me3
- R-loop dysregulation may contribute to EZH2-driven cancers
Reference:
Crossley et al. 2019, Molecular Cell
Garcia-Muse and Aguilera, 2019, Cell
Wells et al. 2019, Trends in Cancer
Santos-Pereira and Aguilera, 2015, Nature Reviews Genetics

CUT&Tag-IT® R-loop Service Data
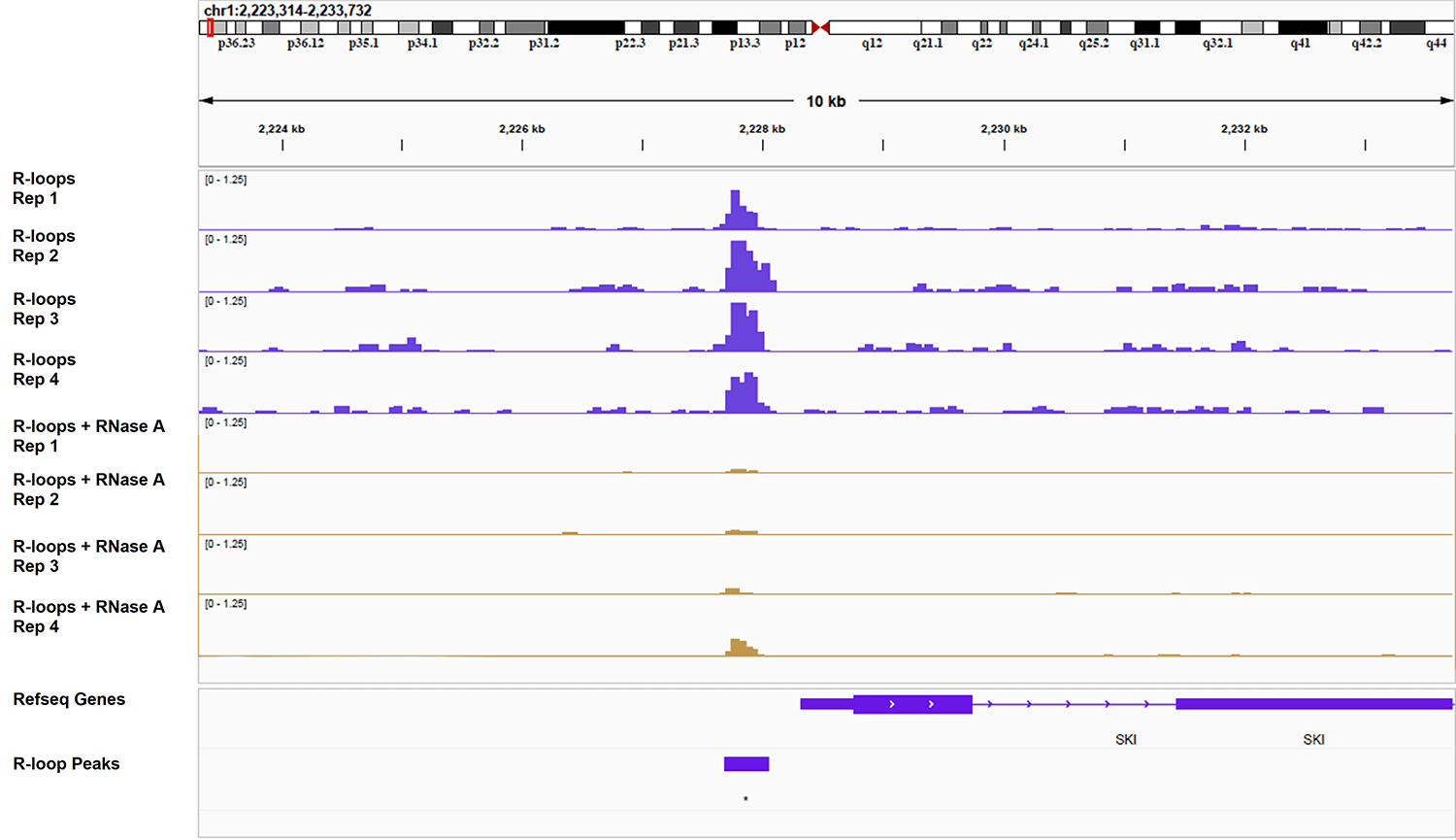
Figure 1: Active Motif CUT&Tag-IT R-loop Services assay shows specificity for R-loops
The CUT&Tag-IT R-loop Service was conducted on four technical replicates of cryopreserved K562 cells (400 K) both with and without RNase A treatment. RNase A is expected to digest away R-loops thus reducing signal. The RNase A treatment clearly results in a dramatic decrease in signal, demonstrating that the CUT&Tag-IT R-loop Assay Kit specifically detects R-loops.
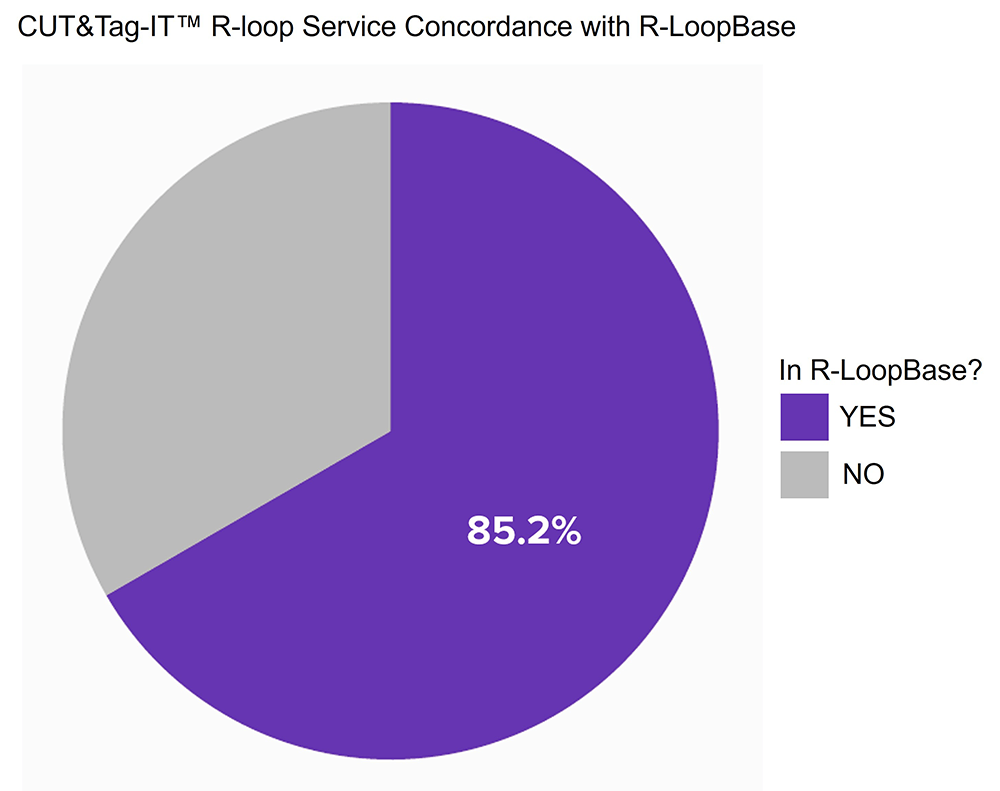
Figure 2: R-loops identified by CUT&Tag-IT R-loop Services assay show high concordance with data from RloopBase
Here, R-loops were identified as peaks that were clearly reduced after RNase A digestion. 85.2% of Active Motif identified R-loops have also been recorded by RloopBase. Assay was conducted with technical replicates of cryopreserved K562 cells (400 K) both with and without RNase A treatment and then sequenced to 30 million Reads. RloopBase: https://rloopbase.nju.edu.cn
CUT&Tag-IT® R-loop Service Documents
CUT&Tag-IT® R-loop Service Sample Submission Portal
Our online sample submission portal allows you to easily upload your service project samples and track your project status. Follow the sample submission instructions in the portal to ensure that all your samples arrive at Active Motif in the best possible condition and properly associated with your project.